What is forex trading?
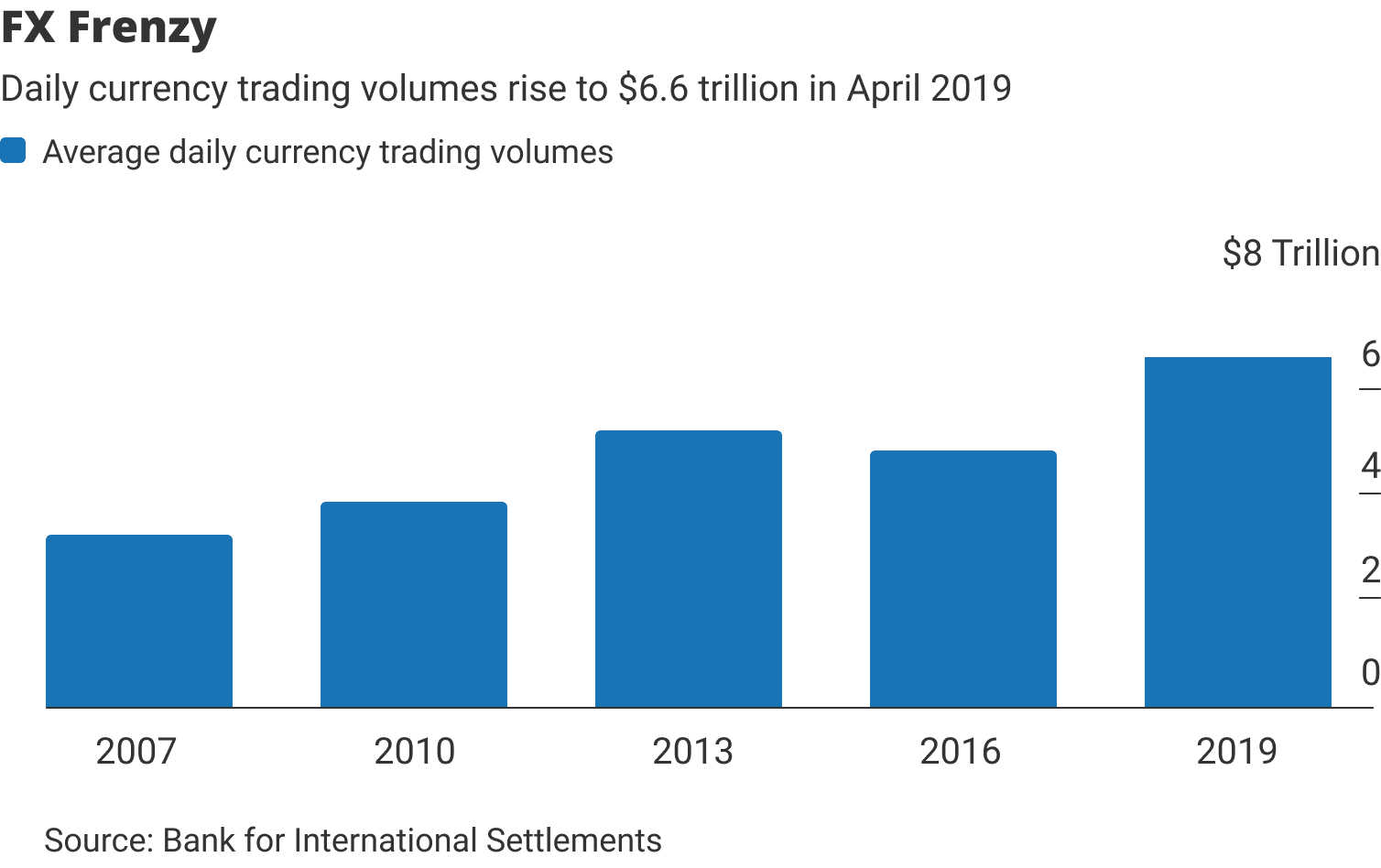
The foreign exchange (forex) market isaglobal decentralized market inwhich national currencies are traded against each other. The daily trading volume on the forex market amounts to $6.6 trillion. This makes Forex by far the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
Forex trading means buying and selling currency pairs with the goal to profit from future price changes. A forex trader will make a profit by buying a currency pair at a market price and selling it later at a higher price, or, alternatively, by selling at a market price and buying it back later at a lower price.
Forex market operates 24 hours a day, each business day, which makes it a truly global financial market. Forex trading involves market participants of different sizes ranging from as large as multibillion-dollar hedge funds and money management funds to as small as individuals trading for their own account —all connected together in real time through electronic communications networks (ECN).
Essentially, al global economies are connected though the forex market, which facilitates the flow of capital between different countries and asset classes. And, while the vast majority of forex transactions are being done to facilitate cross-border trade and capital flows, such as purchasing foreign goods, services, and financial assets, many day traders speculate in the forex market to make profits.
Forex market is highly volatile, meaning the exchange rates of major currency pairs fluctuate significantly every day, which allows forex traders to make profits daily.
The sheer trading turnover on the forex market makes it highly volatile — the exchange rates fluctuate significantly every day — and it is this volatility that makes forex trading so appealing to day traders, because wider price changes allow for higher profits daily.
What is a currency pair?
The first step in learning the fundamentals of forex trading is to become familiar with the basic convention of how currency pairs are referred to on the market. The following table lists the major global currencies and their standard three-letter codes. These codes have been agreed upon by forex market participants worldwide.
| Currency code | Currency |
|---|---|
| USD | US dollar |
| EUR | Euro |
| JPY | Japanese yen |
| GBP | British pound |
| CHF | Swiss franc |
| CAD | Canadian dollar |
| AUD | Australian dollar |
| NZD | New Zealand dollar |
| ZAR | South African rand |
| SEK | Swedish krona |
| NOK | Norwegian krone |
| BRL | Brazilian real |
| SGD | Singapore dollar |
| MXN | Mexican peso |
| CNY | Chinese yuan |
| HKD | Hong Kong dollar |
| RUB | Russian ruble |
What is an exchange rate?
It is important for you, as a forex trader, to understand the difference between the individual currency and an exchange rate. An individual currency is a financial asset, such as a $1 million cash deposit, which one can hold in a bank. But, an exchange rate refers to the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. There are always two currencies involved in an exchange rate: the price of one currency relative to another.
The exchange rate is the relative price of one currency in terms of another. It is presented as the number of units of one currency (called the price currency) that one unit of another currency (called the base currency) will buy. You can think of the exchange rate as the cost of one unit of a base currency measured in terms of the price currency.
For example, the EUR/USD exchange rate refers to the price of one euro (EUR) measured in terms of the US dollar (USD). The following paragraph explains in detail how to interpret currency exchange rates.
How to interpret exchange rates?
{$settings.site_name}, as a broker, quotes exchange rates using the convention “Base currency / Price currency”. For example, the ticker EUR/USD denotes the exchange rate between the Euro and the US dollar. An exchange rate quote of EUR/USD = 1.2500 means that 1 EUR costs 1.2500 USD (or, equivalently, 1 EUR will buy 1.2500 USD). In this case, the euro is the base currency, and the US dollar is the price currency.

An increase in the EUR/USD exchange rate would mean that the euro costs more, or that more US dollars are needed to buy 1 euro. In other words, an increase in the EUR/USD exchange rate would indicate that the euro has appreciated against the US dollar.
How to profit? Forex trading example
Let’s assume the exchange rate for the EUR/USD appreciates from 1.2500 to 1.3000. This represents a 4 percent appreciation in the euro against the US dollar.
1.3000 + 1.2500 - 1 = 4.00%
Note that in the EUR/USD quote, the USD is the price currency and EUR is the base currency, thus a 4 percent appreciation means that 1 euro has increased in value by 4% in US dollar terms.
A forex trader, expecting the euro to appreciate against the US dollar, could buy EUR/USD currency pair (or, as traders say, open a long position in euro). If the EUR/USD exchange rate rises, the trader will make a profit from the price appreciation.
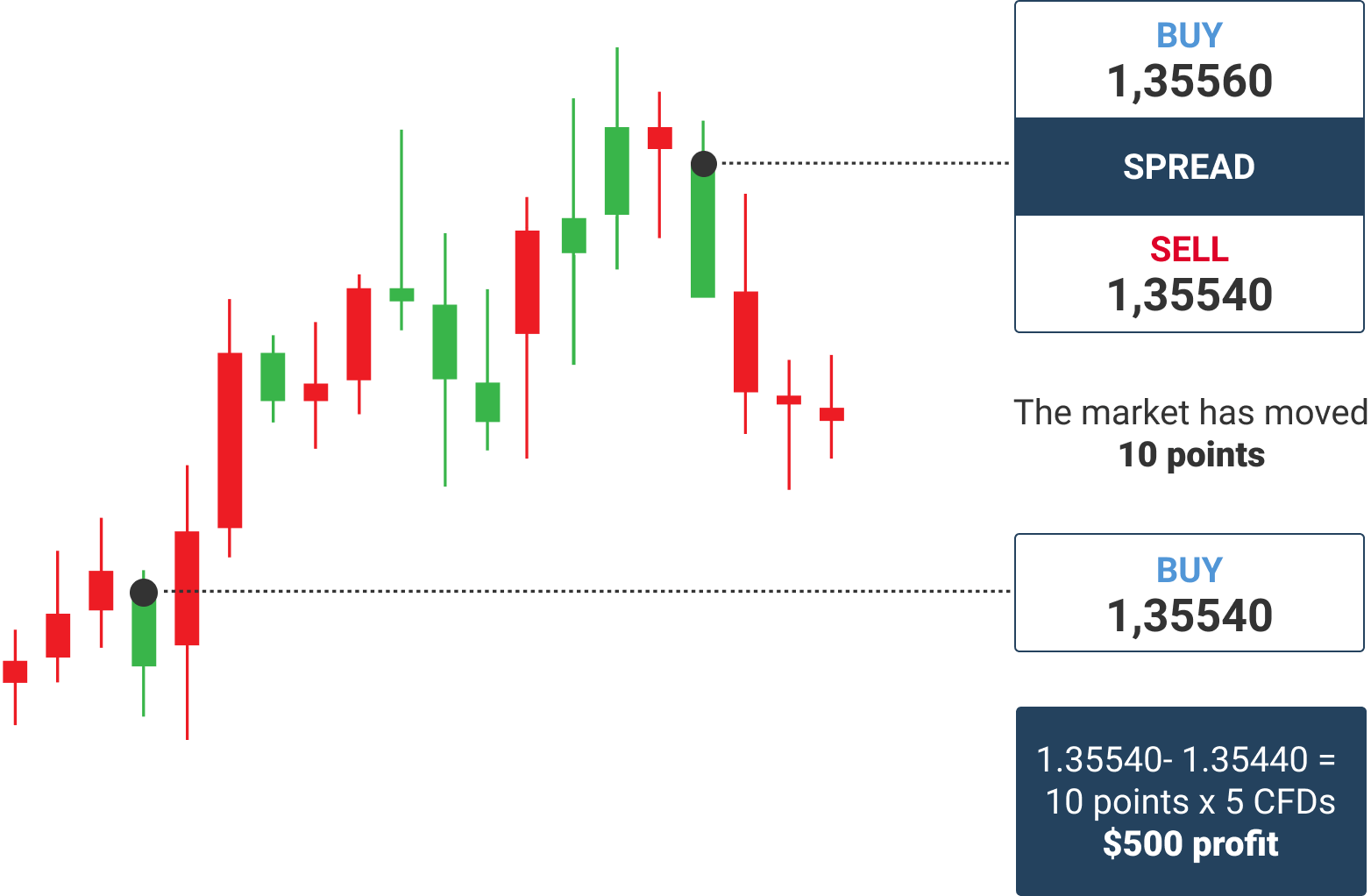
Alternatively, if a trader expects the euro to depreciate against the US dollar, he could sell EUR/USD. In this case, ifthe EUR/USD exchange rate declines, the trader will make a profit from the price depreciation.
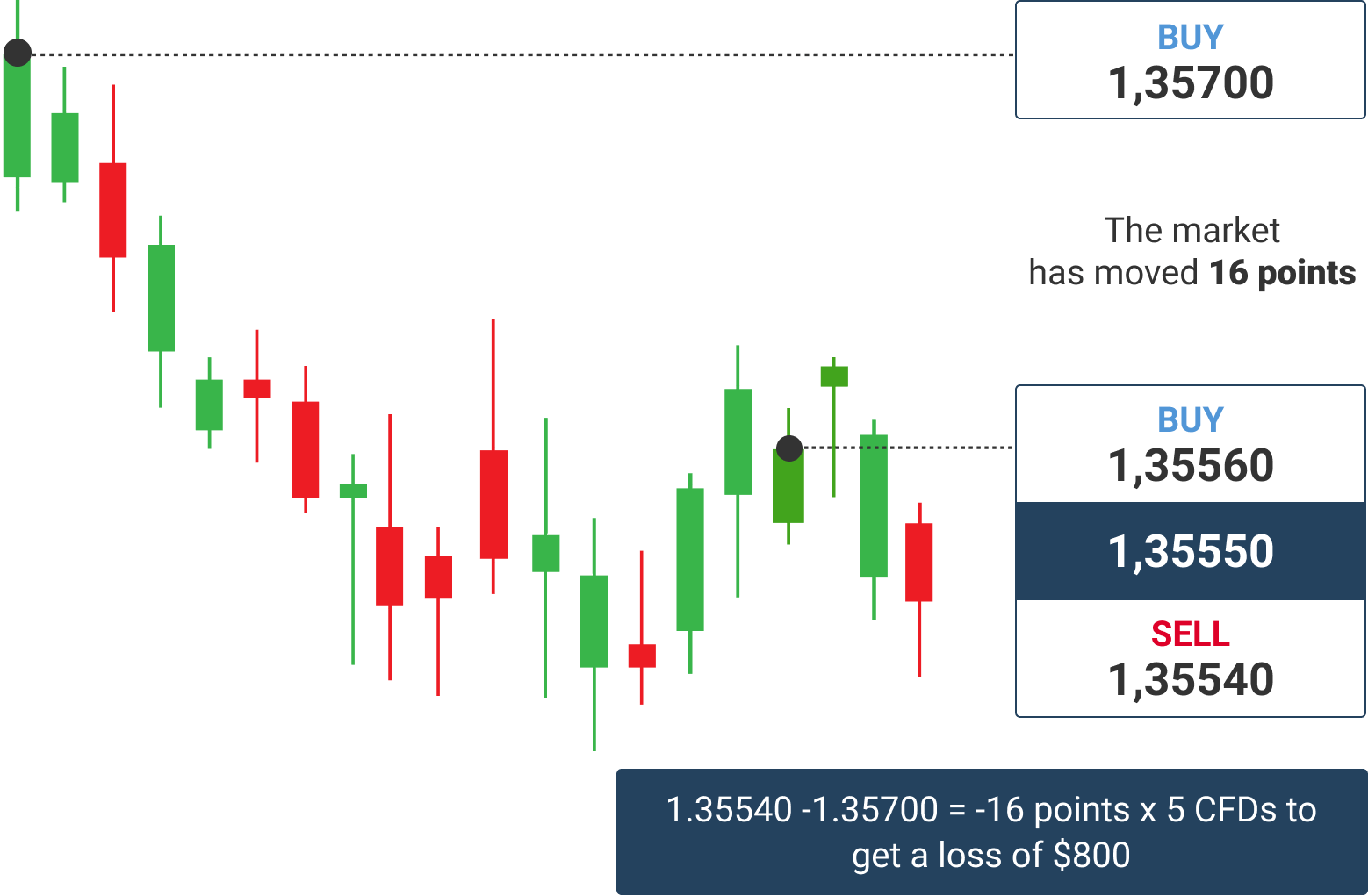
This basic example shows how day traders make profits by trading currencies in the professional forex market.
What is a pip in FX trading?
Pips are units used to measure the change in forex prices. One pip is equal to a one-digit movement in the fourth decimal place of a currency pair.
Note that most major currency exchange rates are quoted to five decimal places. One exception among the major global currencies involve the Japanese yen, for which exchange rates are quoted to three decimal places.
For instance, ifthe euro-dollar exchange rate appreciates from 1.11731 to 1.11741, then ithas increased by 1 pip (equivalent to 0.0001 US dollar). The euro-dollar appreciation by 100 pips would mean an increase in the euro-dollar exchange rate from 1.11731 to 1.12731.
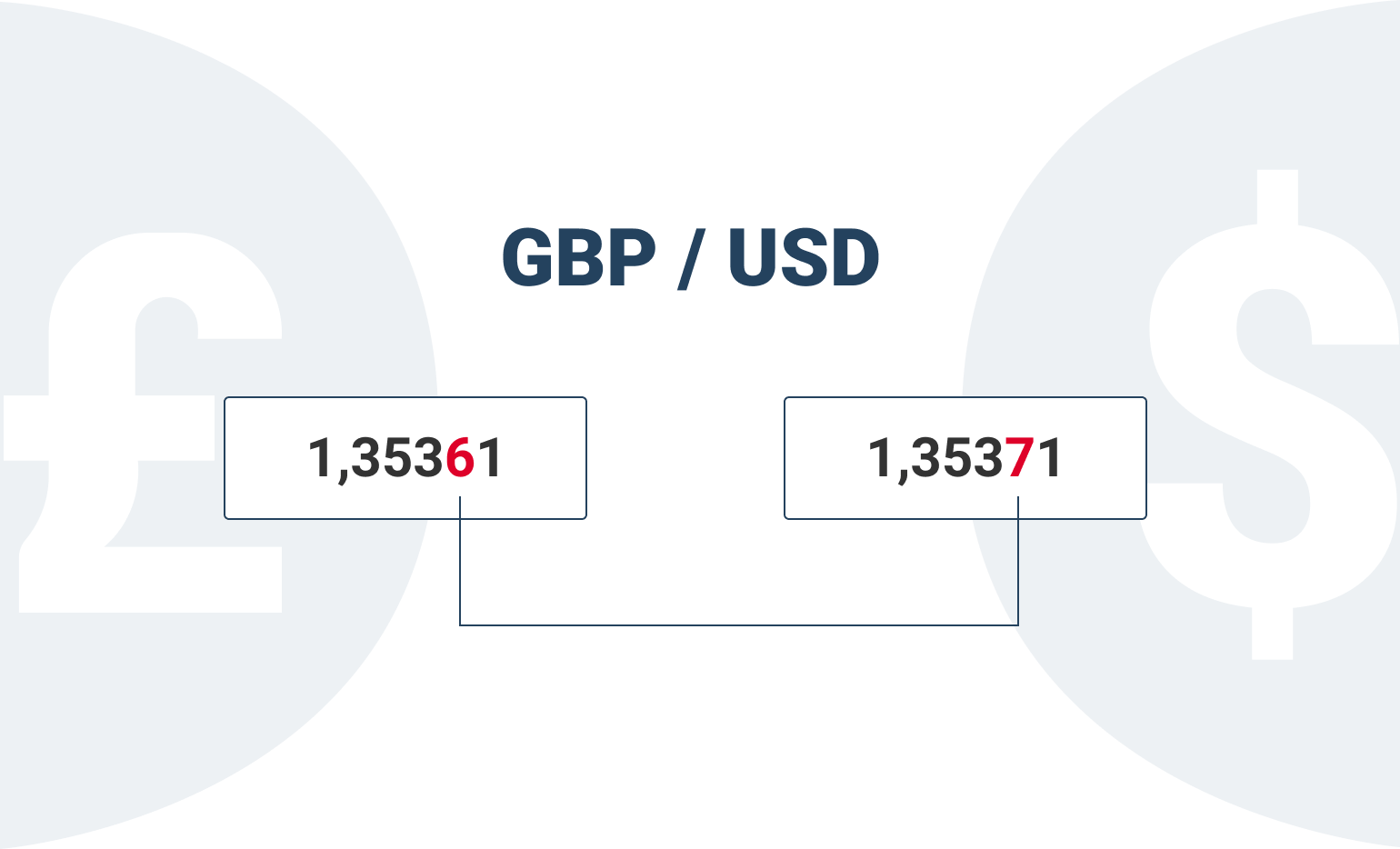
What is Bid/Ask spread in FX trading?
The concept of spread is very important for forex traders to understand.
On the forex market, al currency pairs are quoted using a two-sided price. The “Ask” price — the higher price in the quote —is the price at which you can buy a currency pair. The “Bid” price — the lower price in the quote —is the price at which you can sell a currency pair. The difference between the Bid and Ask prices is called Spread.
А two-sided price in euro—US dollar (EUR/USD) might look like:
1.1205-1.1207
If the trader believes that the EUR/USD price will decline, to profit from this trade idea, he should sell the EUR/USD at 1.1205 (the current bid price). If the price declines, the trader will be able to buy the EUR/USD back at a lower price, and thus make a profit.
Alternatively, if the trader believes that the EUR/USD will rise, to profit from this trade idea, he should buy the EUR/USD at 1.1207 (the current ask price). Ifthe price rises, the trader will be able to sell the EUR/USD at a higher price, and thus make a profit.
Note that the price of any currency pair is shown in terms of the price currency, and that the bid price is always less than the ask price.
One of the core advantages of {$settings.site_name} is narrow spreads. A narrow spread means that the market is liquid and you can quickly open and close positions without incurring significant losses. Also, most trading platforms charge a commission per trade, which can significantly reduce your profits. {$settings.site_name} is a zero-commission trading platform.
What is leverage in FX trading?
Leverage is an important tool, and trading with a 1:100 leverage is a standard practice for forex traders. With leverage you can increase the size of your market position and, as a result, get higher payoffs from small investments.
CFDs on currency pairs are leveraged instruments. This means two things:
-
Buying currencies with leverage requires a low initial outlay.
For instance, with the 100x leverage, you can buy 1 lot of EUR/USD worth 100,000 euro by depositing only 1,000 euro in equity. - Trading with leverage allows you to make substantial gains even from small market moves.
Leverage means that a portion of the position size is financed by borrowed capital, and the trader's equity is ‘leveraged!’ for larger potential profit due to higher position size. Leveraged trading can greatly increase potential profits for a given amount of trader's equity because the trader can buy more with leverage than he or she could otherwise.
For instance, ifthe GBP/USD bought with 100x leverage rises by 1% (from 1.3000 to 1.3130), the trader will get a 100% return on equity in the leveraged position (equal to 1% return times 100x leverage). But, if the GBP/USD declines by 0.5% while the trader holds a long position, the return on the trader's equity will be -50%.
What is margin in FX trading?
The concept of margin is closely associated with the concept of leverage, discussed above. Leverage of 100x means that you need 1/100th (or 1%) of the trade size in equity to enter a trade. In the trading platform, this amount will be shown as margin. The other part, equal to the 99 percent of the trade size, will be financed by {$settings.site_name} (your broker).
The following is a simple example: At {$settings.site_name}, the amount of leverage for EUR/USD is 100x, meaning that a trader must supply only 1% of the purchase price — the initial margin requirement — and the rest 99% will be supplied by us — the broker. 100 leverage = 100% position / 1% margin (equity).
What is a lot in FX trading?
On the forex market, the trading volume is measured in lots. It denotes the amount of base currency measured in terms of the price currency. For example, for EUR/USD currency pair, 1 lot is equal to 100,000 euro (the base currency).
You can buy or sell any amount of lots, including a fractional amount of 1 lot (such as a 0.1 lot). To find out the details about the lot size, the lot step, and the minimum and maximum amount of lots per trade, take a look at our Contract Specifications page.
Forex majors, minors, and exotics:
What is the difference?
The forex market convention is to split al currency pairs into the following categories:
- Forex majors. Seven major currency pairs that make up 70% of the global forex trading turnover: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, USD/JPY, USD/CAD, and AUD/USD.
- Forex minors. Less liquid currencies, quoted either against the US dollar (e.g., US dollar vs Polish zloty, USD/PLN) or as cross-rates (e.g., euro and the Canadian dollar, EUR/CAD).
- Exotics. Thinly traded currencies of emerging economies, such as the USD/MXN (the US dollar against the Mexican peso).
You can trade major, minor, and exotic currency pairs on the {$settings.site_name}'s award-wining, fast and secure trading platform.
What is a cross-rate in FX trading?
A cross-rate is an exchange rate between two major currencies, excluding the US dollar. For instance, the EUR/CAD is a cross-rate between the euro and the Canadian dollar. Given the two major currency pairs, involving the US dollar — the EUR/USD and the USD/CAD — it is possible to back out the cross-rate between the euro and the Canadian dollar:

In the {$settings.site_name}'s trading platform, you can trade al of the most popular forex cross-rates. Below is an example, showing how a trader could profit from trading a EUR/CAD cross-rate.
Let’s assume that a trader conducts fundamental analysis and concludes that the economic activity in the Eurozone is accelerating, while the Canadian macroeconomic indicators show a decelerating economy. The trader concludes that the euro is expected to strengthen, while the Canadian dollar is expected to weaken.
To benefit from this market outlook, the best option would be to buy the EUR/CAD. According to the trader’s outlook, the euro is expected to appreciate, while the Canadian dollar is expected to depreciate, which will reinforce the upwards trend in the EUR/CAD and produce substantial profits for a long position in the EUR/CAD cross-rate.
How does the Forex market work?
Forex market facilitates cross-border trade and capital flows, where companies and individuals need to make foreign currency transactions. Trade flows cover such transactions as imports and exports of goods and services, and cash spending by tourists traveling abroad.
And, although trade flows comprise a significant proportion of the daily turnover in the forex market, an even larger proportion is accounted for by cross-border capital flows. These types of transactions include investments in foreign financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and other financial assets denominated in foreign currencies, as well as direct investments in foreign operations by companies.
This flow of money across international markets generates a huge and growing forex trading turnover. For 2019, the global daily forex turnover is estimated at $6.6 trillion, which makes forex the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
Every forex transaction requires that one currency be exchanged for another, and exposes market participants to the risk that the exchange rate will move against them. Most market participants, such as corporations and banks, reduce this foreign exchange risk through hedging.
In contrast to corporations and banks, day traders are active FX market participants. They build short-term price forecasts based on trading strategies, and then open market positions to profit from their forecasts. Strict risk-management controls and rules-based trading systems (trading plans) are critical to success in day trading, especially when leverage isinvolved.
Who are the biggest players
in the Forex market?
There is an extremely diverse list of market participants, trading in the forex markets, ranging in size from multi-billion-dollar actively managed hedge funds down to small brokerage accounts of individual traders.
There are four main groups of forex market participants. They are (in descending order of trade volume):
- Financial investors holding real money FX accounts, buying and selling securities in foreign currencies. 45% of the forex market is being driven by dealing banks, foreign currency broker- dealers, and institutional investors.
- Corporations holding corporate FX accounts, conducting global business and selling goods and services across borders.
- Professional day traders holding retail leveraged accounts.
- Central banks holding FX reserves and conducting monetary policy.
Corporations
Corporations of al sizes buy and sell foreign currency to finance their cross-border purchases and sales of goods and services. Usually, corporations undertake these FX transactions through the large FX trading banks (such as HSBC, Deutsche Bank, UBS and Citigroup). Many corporate foreign exchange transactions also relate to cross-border investment flows, such as mergers and acquisitions (M&A), capital investments, and foreign-currency borrowing.
Financial investors
Financial investors, holding real money FX accounts, include investment funds, mutual funds, pension funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other institutional investors. These investors are referred to as real money because they usually have low-risk investment policies and do not use leverage or derivative products in their FX investments.
Professional day traders
Professional day traders are individuals actively trading for their own accounts with the use of leverage and CFDs. The emergence of electronic communications networks (ECN) technology has prompted a huge surge in speculative trading activity by retail traders globally.
ECN technology has significantly reduced the barriers to enter the forex market and enabled retail traders to generate significant profits through active trading. Currently, the community of professional FX day traders accounts for about 10 percent of daily FX market turnover, and this share continues to grow.
Professional day traders apply a wide array of trading styles and strategies.
- Fundamental analysis. Some FX traders apply fundamental analysis and open longer term FX positions based on their views of macroeconomic trends in a particular economy. They analyze trends in key macroeconomic indicators and identify their impact on the underlying currency.
- Technical analysis. Others are active day traders that use technical trading strategies {such as those based on moving averages, oscillators, or support and resistance levels) and whose trading cycles are often measured in seconds or minutes.
Importantly, the majority of retail accounts trade with leverage. Leverage is usually applied by professional traders, consisting of hedge funds and active day traders.
Central banks
Central banks, such as The Bank of Japan, The European Central Bank, and The Federal Reserve System of the USA, often intervene into forex markets and may cause significant deviations in exchange rates. Central banks influence the exchange rates of their respective domestic currencies by conducting open market operations, changing short-term interest rates, or by increasing their foreign exchange reserves.
The foreign exchange reserves of some countries are enormous, which allows them to influence the level and trend of foreign currency exchange rates as part of pursuing their public policy goals.
For example, ifthe central bank believes that its domestic currency has become too strong to the level that it undercuts that country’s competitiveness on export markets, the central bank can intervene by selling its domestic currency to exert a downward pressure on its exchange rate. The Bank of Japan intervened in the USD/JPY market in 2004 and 2010 by selling yen against the US dollar to cause it exchange rate depreciation.
Forex traders, especially those trading with long-term forecast horizons, analyze monetary policies conducted by major central banks, and try to understand how the actions of central banks will influence the exchange rates in forex markets.
There is an extremely wide variety of forex market participants with differing objectives, ranging from making a speculative profit through day trading, to hedging risks, to conducting business transactions in foreign currencies. This complex, global interaction of forex market participants creates the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, and allows day traders to make substantial profits daily from speculation on currency price changes.
What hours of the day can you trade Forex?
Unlike any other market, the currency market operates 24 hours a day during the business week. There are four major trading sessions on the forex market: Tokyo, Sydney, London, and New York. The forex market operates as a global network of electronically connected broker-dealers, exchanges, and banks from al over the world.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day from 17:00 (EST) on Sunday until 16:00 (EST) on Friday, 5 business days a week. The only gap on forex occurs on the weekend. The international scale of the forex market implies that there is always high liquidity and sufficient supply and demand to satisfy virtually any trade size at any time throughout the day. It is this global scope and high liquidity that makes the forex market so attractive to day traders.
| Local time | GMT |
|---|---|
|
Sydney open - 07:00 Sydney close - 16:00 |
22:00 - 07:00 |
|
Tokyo open - 09:00 Tokyo close - 18:00 |
00:00 - 09:00 |
|
London open - 08:00 London close - 16:30 |
08:00 - 16:30 |
|
New York open - 08:00 New York close - 17:00 |
13:00 - 10:00 |
The forex market is most active during the North American (New York) trading session, the European (London) trading session, and the Asian (Tokyo) trading session. When corporations and banks located in these financial centers are conducting business activities, and their sock markets are open, the forex market has the highest liquidity.
When these sessions overlap, there may be particularly strong movements in exchange rates of respective currencies. For example, when the European and American trading sessions overlap, there may be particularly high volatility and strong trends in EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF currency pairs.

When is the best time to trade forex?
The largest share of global forex trading occurs in London (UK), followed by New York (USA). Meaning the highest liquidity on the forex market can be observed between 8:00 a.m. and 11:30 a.m. New York time, when both financial centers are open, which is the best time to trade on the forex market. New York is the second largest forex trading hub, followed by Tokyo.
What are the most popular currency pairs?
There are four most popular currency pairs globally, which have the largest daily trade volumes on the forex market: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF. These currency pairs have some of the lowest spreads, as compared to some of the more exotic forex trading pairs, which maximizes the profitability of trading in these pairs and allows to apply certain highly profitable day trading strategies, such as scalping.
The following table lists the top five most popular forex pairs, as measured by their share of daily global forex turnover:
The most popular currency pairs by daily global trading turnover
| FX Ticker | Name Convention | Share in global trading turnover |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | Euro | 28% |
| USD/JPY | Dollar—Yen | 14 |
| GBP/USD | Sterling | 9 |
| AUD/USD | Aussie | 6 |
| USD/CAD | Dollar—Canada | 5 |
Note that 85% of daily turnover in forex markets involve the US dollar, and each of the most popular currency pairs includes the US dollar (USD).
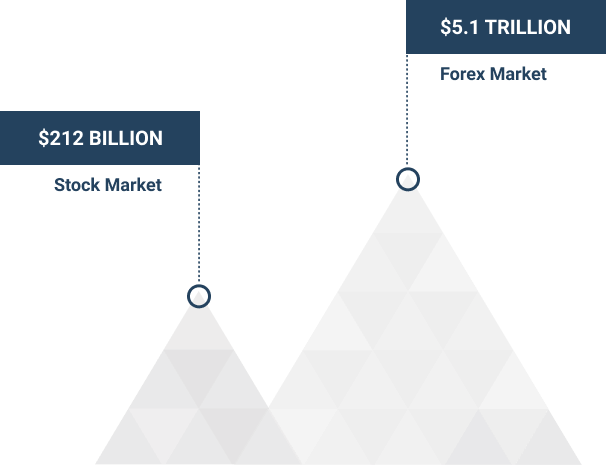
How liquid is the Forex market?
The Forex market has the largest daily trading turnover in the world estimated at $6.6 trillion as of 2019. For comparison, the global daily turnover in forex market is about 50 times larger than daily turnover in equity markets, and about 15 times larger than daily turnover in bond markets.
The history of the Forex market
In the wake of the Bretton Woods Agreement a new monetary system was established, in which the exchange rates of al major currencies were predetermined (locked) against the US dollar. The US dollar in turn was convertible into gold at a price of $35 per ounce. This was known as the gold standard, under which major fiat currencies could be converted into a pre-specified amount of gold. This attempt to lock currency exchange rates ended when the President Richard Nixon unilaterally announced, in August 1971, to suspend the convertibility of the US dollar into gold.
Today, in al major economies, money is not convertible into anything else, but it is, in law, legal tender, meaning fiat money derives its value via government decree and must be accepted when offered in exchange for goods and services.
The decision to abandon the gold standard marked the creation of the modern fiat currency regime of floating exchange rates. Today, more than $6.6 trillion is transacted each day ina freely traded foreign exchange market (also known as the FX, or forex market).
What moves Forex currency pairs?
To understand the fundamental factors driving forex currency pairs, FX traders apply fundamental analysis. There are three main fundamental factors underlying changes in foreign currency exchange rates in the short-term:
- Changes in interest rates
- Changes in inflation
- Changes in trade and capital flows
Once the major economies have moved to a system of fiat currencies in August 1971, the role of central banks, as the monopoly suppliers of that currency, has become crucial. In modern economies, therefore, central banks play a crucial role in determining currency exchange rate moves in order to maintain price stability and economic growth.
Changes in interest rates
Central banks change official interest rates (or policy rates) to influence the demand for money by banks, corporations and individuals in order to stimulate real economic growth. Therefore, changing interest rates is the primary monetary policy tool being used by most central banks.
Suppose that the Federal Reserve System, the central bank of the USA, has announced an increase in the federal funds rate — the official interest rate used in US monetary policy. This rate, also known as the fed funds rate, is the interbank lending rate, at which member banks can borrow USD reserves directly from the Federal Reserve System. The target for the fed funds rate is decided on and announced by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) at its meetings held every six weeks.
An increase in the fed funds rate will increase the base rates for USD-denominated deposits at commercial banks, as well as the yields on USD-denominated bonds.
The increase in yields of USD-denominated corporate and government bonds will make them more attractive to global investors. In order to buy those bonds, a global investor has to exchange his domestic currency into the US dollars.
Therefore, al else being equal, rises in the federal funds rate will cause the US dollar to strengthen. To profit from that event, a forex trader could open a short position in the EUR/USD or GBP/USD —sell euro or pound against the US dollar, respectively.
As another example, consider the trend in the EUR/USD from 2005 to 2009 and the trend in the European Central Bank’s official policy rate known as the refinancing rate. During the period from 2006 to mid- 2008, the former ECB’s President Jean-Claude Trichet surprised the market with a series of European interest rate hikes. This drove the EUR/USD to rise (the euro to strengthen against the US dollar) by 33%, from 1.2 to 1.6, over that same period.
The impact of changes in interest rates by central banks can be generalized as follows:
E.g., a surprise rise in the federal funds rate, announced by the FOMC, will cause the US dollar to strengthen relative to other major currencies.
The following table shows interest rate indicators for each major country, and the currency pairs affected when a central bank’s decision is announced.
| Economy | United States | European Union | Japan | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic indicators | Fed Interest Rate Decision | ECB Interest Rate Decision | BoJ Interest Rate Decision | BoE Interest Rate Decision |
| Major currencies affected |
EUR/USD GBP/USD AUD/USD USD/CHF USD/JPY USD/CAD |
EUR/USD | USD/JPY | GBP/USD |
| Importance | High | High | High | High |
Changes in inflation
The laws of supply and demand state that scarcity makes a particular asset more valuable, while abundance diminishes value. This is true for currencies, where excess supply of a particular currency leads to inflation in an economy, and depreciation of that currency’s exchange rate against other inflationary- stable currencies.
When the money supply of one currency expands more rapidly than that of another, the exchange rate of the first currency will tend to depreciate against the second.
Surprise rises in inflation or money supply will weaken the currency. Forex traders, therefore, closely monitor such economic indicators as CPI (consumer price index), PPI (producer price index), and M2 (narrow money supply), available for currencies of al major economies.
Forex traders monitor macroeconomic indicators for the world's largest economies, such as the USA, European Union, United Kingdom, Japan and China to be able to trade the EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CNH, respectively. Analysis of economic indicators is an indispensable tool that forex traders use in fundamental analysis of forex markets.
You can monitor actual vs. consensus (forecast) values of most popular macroeconomic indicators right in the {$settings.site_name}’s trading platform by clicking Analytics —> Economic Calendar. To analyze changes in inflation and money supply of forex exchange rates, review the following indicators:
| Economy | United States | European Union | Japan | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic indicators |
|
|
|
|
| Major currencies affected |
EUR/USD GBP/USD AUD/USD USD/CHF USD/JPY USD/CAD |
EUR/USD | USD/JPY | GBP/USD |
| Importance | High | High | High | High |
Changes in trade and capital flows
The third important currency driver is global trade. Global trade has soared over the past two decades thus driving the volumes of foreign currency transactions. In fundamental analysis, trade is defined as the difference between exports and imports (net exports), and is a component of GDP.
When a country exports goods, foreign buyers need to buy the currency of the exporter (i.e. domestic currency). When a country imports goods, the importer has to buy the foreign currency of the foreign seller by selling the domestic currency.
Thus, ifnet exports ispositive, meaning the country has a trade surplus, it will drive demand for the domestic currency. Otherwise, if net exports isnegative, the country has a trade deficit, and it will diminish demand for the domestic currency.
The surprise changes in a trade surplus or a trade deficit, therefore, can instantaneously change the exchange rate of a domestic currency against foreign currencies based on expectations of changes in demand for a domestic currency.
| Economy | United States | European Union | Japan | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic indicators |
|
|
|
|
| Major currencies affected |
EUR/USD GBP/USD AUD/USD USD/CHF USD/JPY USD/CAD |
EUR/USD | USD/JPY | GBP/USD |
| Importance | High | High | High | High |
How to project currency exchange rates?
Forex market is a freely traded global financial market, in which willing buyers trade with willing sellers. Therefore, exchange rates of major currency pairs are determined by market supply and demand. Changes in supply and demand cause changes in exchange rates.
To project future exchange rates of currency pairs, forex traders apply two analytical approaches:
- Technical analysis
- Fundamental analysis
Technical analysis is widely used to make short-term price forecasts, which is especially relevant to forex day traders. It is based on analysis of price charts, trading volumes, chart patterns, and a wide range of technical indicators.
Fundamental analysis provides the backdrop for forecasting long-term levels and trends in currency exchange rates. Fundamental analysis involves the analysis of economic news and monitoring of major macroeconomic indicators of the world's largest economies. More advanced traders analyze monetary policy tools being used by major central banks, which significantly affect currency exchange rates.
How to apply fundamental analysis in FX trading?
Forex day traders keep track of the following three main economic indicators that drive forex exchange rates:
| Indicator | Changes ininterest rates | Changes ininflation | Changes intrade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact on FX rate | Currencies with higher interest rates are more attractive | Currencies with lower inflation are more attractive | Countries that are major net exporters have more attractive currencies |
| Economic reasoning | Short-term changes in interest rates are the paramount factor in currency valuation. Forex traders look at most other economic indicators primarily to predict how a central bank will respond with interest rate changes in the future. Surprise changes in interest rates affect currency exchange rates the most. | Inflation isthe second most important driver of currency exchange rates. The excess supply of a particular currency leads to inflation in an economy, and depreciation of that currency’s exchange rate against other inflationary-stable currencies. Most developed economies target 2% inflation. | The currencies of countries with a steady trade surplus are expected to appreciate against foreign currencies. In contrast, the currencies of countries with steady trade deficits are expected to depreciate in value. Forex day traders monitor trade balance indicators of all major world economies to forecast future forex rates. |
How to apply technical analysis in FX trading?
Technical analysis is a very powerful tool in forecasting exchange rate moves. In fact, technical analysis is the only way to analyze forex, cryptocurrency, and equity markets for intraday trading. The essence of technical analysis is studying price charts using technical indicators with the goal to eliminate market noise and identify the true direction of the price trend.
The primary tools used in technical analysis are charts and technical indicators. Charts are the visual display of historical price and volume data of aparticular financial instrument (currency pairs in case of forex market), and can be accessed in the trading platform. Traders analyze price charts using trend lines and technical indicators, trying to identify chart patterns and profitable trade setups.
Technical indicators are powerful analytical tools, based on mathematical formulas, allowing to make accurate price forecasts. Technical indicators are built into the trading platform. When a trader adds a particular indicator to the chart, it transforms the price data and often generates a trade signal, thus assisting the trader to make a trading decision.
Oscillators are another type of technical indicator measuring the market volatility and helping traders to identify the best market entry and exit points. Traders often combine the use of oscillators and trend indicators in a single trading strategy to make better trading decisions.
Trend channels and trend lines represent the main drawing tools that traders apply to the price chart to identify the underlying price trend in the market. Linear equidistant channel and the linear regression channel are some of the examples of powerful forecasting tools in forex trading.
Overall, technical analysis includes a powerful analytical toolbox allowing traders to make better trading decisions and earn higher profits from forex trading.
What is a forex trading strategy?
Based on technical analysis, forex traders create and use trading strategies, based on specific technical indicators, trading signals, and risk management rules. Trading strategy is a plan, which allows you to make trading decisions based on exact signals and risk-management rules, rather then on random guess or market noise. Having a rules-based trading plan allows forex traders to achieve consistency and profitability in trading.
Trading strategy is what differentiates the top 5% of successful forex traders from the bottom 95%. The top 5% of forex traders have a profitable trading system that generates consistently accurate trading signals for them, while the bottom 95% of traders do not have such a system.
A trading strategy, producing accurate trade signals, is one of the most important factors that will make you a successful forex trader. Every trading strategy is based on a particular set of technical indicators, chart patterns, and other tools, suggesting to a trader when to buy or sell a currency pair.
As in any profession or business, strategy and discipline are some of the most important factors for success, and forex trading is not an exception.
What is a trend on the forex market?
Forex markets are very complex due toa variety of intertwined fundamental factors affecting currency valuations every day. In addition, every currency pair consists of two currencies, with each having its own supply and demand dynamics, which makes the analysis even more difficult. Therefore, forex traders apply trend-following trading strategies to profit from existing market trends.
he goal of a day trader is to identify the current direction of price changes and then follow the trend. Approximately 70% of time prices are in a trend mode, either up or down, and 30% of time they are flat.
hus, day traders that become skilled at identifying trends, are able to buy at low prices and sell at higher prices, thus making money on forex markets. In order to become skilled at identifying trends, forex traders learn to apply technical analysis.
How to manage risks in forex trading?
One of the key factors to success in forex trading is effective risk management, which involves:
- Diversification, and
- Setting stop-loss orders
What is diversification in FX trading?
The concept of diversification relates to risk management and means that you shouldn't invest al capital in asingle asset. Or, equivalently, ifyou’re aforex day trader, you shouldn’t trade ona single currency pair.
Diversification will help you to avoid disastrous outcomes for your trading account. A perfect example would be trading in USD/CHF in January of 2015, when its price dropped approx. 25% in a single day, which is enormous taking into consideration the effect of leverage.
So, lots of forex traders trading on margin have lost their deposits. They could have avoided this disastrous outcome ifthey had diversified their trading into another currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD.
The best practice is to avoid trading on a single currency pair. Instead, select the top 5 most liquid currency pairs and trade them al. You can also add other asset classes to your trading portfolio, such as equities, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. With diversification, your profitability from trading will be more safe and consistent.
What is a stop-loss order in FX trading?
Which way to trade forex is better: Spot market or forex CFDs?
Spot Forex
In spot markets, traders agree to directly exchange two currencies at an agreed price. A spot transaction involves a direct exchange of cash. For instance, a spot transaction in EUR/USD pair involves buying of euro against selling the US dollar at a market price with immediate settlement in cash.
Spot transactions are usually conducted by large dealing banks and corporations. Day traders usually do not trade on spot forex markets due to wider spreads and higher trading costs, compared to trading in forex CFDs.
CFD Forex
A CFD is a highly popular financial instrument designed specifically for day trading. A CFD (Contract for Difference) is a derivative product, where two parties agree to pay each other the difference in price of an underlying asset, between the time of purchase and sale {open and close) of the position.
CFDs are cash-settled forward contracts, highly leveraged, allowing to open long and short positions with a small initial outlay. Trading in forex CFDs provides certain significant advantages:
- The ability to open long and short positions, without any borrowing costs.
- High leverage of up to 1:100.Leverage is a powerful tool, allowing you to increase thes izeofy our trade by borrowing a portion of the trade value from {$settings.site_name}. This allows you to increase potential profits (and losses) given the same amount of initial outlay (initial margin), and amplify your wins and return on capital.
- Noneed to buy or sell the actual (underlying) currency. CFDs are derivative products.
- Extremely high liquidity, tight spreads and no commissions.
- Trading is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.
As a result, the majority of total daily turnover in the global FX market is made up by CFD trading, while spot transactions account for only 35% of total daily turnover.
How to start trading Forex CFDs today?
To become a forex trader you have to open a brokerage account at {$settings.site_name}. Follow these two simple steps:
- Sign up at {$settings.site_name} to create a trading account.
- Deposit funds to your trading account.
Then you will obtain access to the {$settings.site_name}’s trading platform and will be able to buy and sell forex pairs.
Why trade CFDs with {$settings.site_name}?
- {$settings.site_name} is a CFD trading platform, which lets you speculate on the most popular CFD markets — Forex, Cryptocurrencies, Indices and Commodities Markets — long and short, with up to 100x leverage. With {$settings.site_name}, you can trade at any time throughout the day, seven days a week, from any web-browser.
- Trading CFDs with {$settings.site_name} is simple, yet powerful. It allows you to analyze different financial markets and execute trades within an easy-to-use, one-click trading interface.
- Make accurate price forecasts by analyzing beautiful charts using the {$settings.site_name}’s CFD Trading Platform. There are more than 70 technical indicators, 6 chart types, and 9 timeframes available in the trading platform.
- Maximize your profitability by trading CFDs with low commissions and tight spreads.
Risk Disclosure
According to the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), between 74-89% of retail investors lose money when trading in CFDs. You should consider whether you understand the basics of CFDs, how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to assume the risks of losing your money in CFD trading.
While trading in CFDs, it is possible to lose the entire invested capital due to leverage rapidly. In this respect, investors should have appropriate financial means and the ability to bear such loss.
Why trade Forex with Us?
- 24/7 Customer Support
- Personal Account Manager
- Reliable custody of funds
- Up to 400x leverage
- 0% commissions /low spreads
- Daily market analyses and trading ideas
- 70 technical indicators
- 6 Chart types
- 9 timeframes
- Trading Academy
- Webinars
- Step-by-step guides and free courses